Understanding Fluency

What is Fluency?
Fluency is being able to read with automaticity. A fluent reader reads with rate, accuracy, expression, and intonation.
How is Fluency Taught?
Fluency is incorporated throughout the course as students practice reading their weekly stories and independent reading stories daily using rate, accuracy, intonation, and expression. Fluency recording assignments are started in First grade. In addition to fluency recordings, specific fluency skills are taught in the second and third grades in targeted lessons throughout the course.
Examples of how fluency is taught in the K-3 Language Arts courses are below:
Reading Text
Students learn about fluency through reading text within the lesson. For example, in the third-grade lesson below students learn about reading fluently by reading about rate, expression, and intonation. They listen to an example of a fluent reader and complete their own fluency recording.
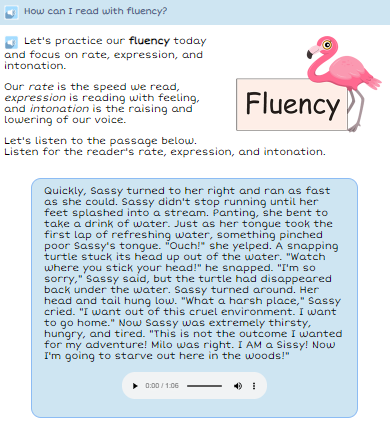

How do students practice Fluency?
Students practice fluency daily in grades K-3 as they practice reading the weekly story from the lesson. Students also complete a weekly recording of themselves reading their selected independent reading story for that week. Below is a link to a weekly story from second grade.
Weekly Story: Pixie’s New Home
The directions and rubric for the weekly practice fluency assignment related to the weekly story are shown below:

Rubric
| Expression and Volume (5) | |||
|---|---|---|---|
| Reads in a quiet voice as if to get words out. The reading does not sound natural like talking to a friend. | Reads in a quiet voice. The reading sounds natural in part of the text, but the reader does not always sound like they are talking to a friend. | Reads with volume and expression. However, sometimes the reader slips into expressionless reading and does not sound like they are talking to a friend. | Reads with varied volume and expression. The reader sounds like they are talking to a friend with their voice matching the interpretation of the passage. |
| Phrasing & Intonation (5) | |||
| Reads in a monotone voice. | Reads in two or three word phrases, not adhering to punctuation, stress and intonation. | Reads with a mixture of run-ons, mid sentence pauses for breath, and some choppiness. There is reasonable stress and intonation. | Reads with good phrasing; adhering to punctuation, stress and intonation. |
| Smoothness (5) | |||
| Frequently hesitates while reading, sounds out words, and repeats words or phrases. The reader makes multiple attempts to read the same passage. | Reads with extended pauses or hesitations. The reader has many “rough spots”. | Reads with occasional breaks in rhythm. The reader has difficulty with specific words and/or sentence structures. | Reads smoothly with some breaks, but self-corrects with difficult words and/or sentence structures. |
| Pace (5) | |||
| Reads slowly and laboriously. | Reads moderately slowly. | Reads fast and slow throughout reading. | Reads at a conversational pace throughout the reading. |
| Total: 20 | |||
How is Fluency Assessed?
Fluency is assessed throughout the course as students complete fluency recordings for the teacher to listen to and assess. Below is an example of a fluency check assessment:

Rubric
| Rate (4) | |||
|---|---|---|---|
| The passage is read with long extended pauses or by slowly sounding out each word. | The passage is read either too quickly or too slowly. | The passage is mostly ready smoothly. | The passage is read smoothly and continuously. |
| Expression (4) | |||
| The passage is read without expression. | The passage is read with limited expression that may not match the text meaning. | The passage is read with expression that adds some emphasis to the text. | The passage is read with expression that adds dramatic emphasis to the text. |
| Intonation (4) | |||
| The passage is read in a monotone voice. | The passage is read with limited changes in voice pitch that may not match the text meaning. | The passage is read with appropriate changes in voice pitch that reflect some comprehension of the text. | The passage is read with appropriate changes in voice pitch that reflect clear comprehension of the text. |
| Total: 12 | |||
